Hammurabi of Babylon: The Legendary Ruler of Ancient Mesopotamia
At this point in history, a formidable leader emerged on the scene—Hammurabi, the Amorite king of Babylon, who ruled from 1792 to 1750 BCE. Widely considered one of the most influential rulers of the ancient Mesopotamian world, Hammurabi's reign marked a turning point in the region's history. He successfully expanded Babylon's influence by conquering or destroying many of the major Mesopotamian cities. His military campaigns were relentless, and his strategic acumen led to the subjugation of the Assyrian kingdom and the extension of Babylon's power as far west as Syria. With these achievements, Hammurabi laid the foundations for the Babylonian Empire.
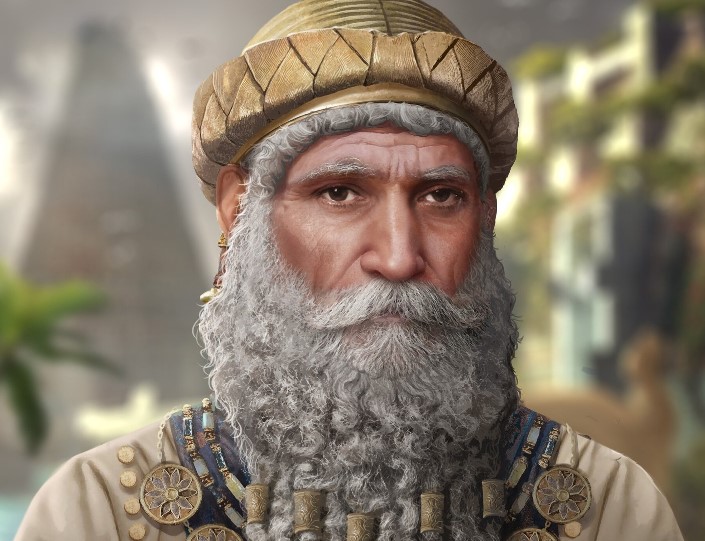

Hammurabi
The Code of Hammurabi: A Legal Milestone
Hammurabi is perhaps best known for the introduction of the "Code of Hammurabi," one of the most comprehensive legal documents of the ancient world. Inscribed on a towering stone stele over two meters high, this code is not the oldest legal text from Mesopotamia but certainly the most extensive and thorough. The stele's inscriptions outline a wide range of laws governing various aspects of daily life, including commerce, property rights, family matters, labor disputes, and criminal justice.
The significance of the Code of Hammurabi lies not only in its detailed regulations but also in its role as a unifying force across the diverse regions of his empire. By codifying laws that applied to everyone under his rule, Hammurabi sought to create a sense of order and justice, ensuring that legal disputes could be resolved according to a consistent set of principles. The code established the concept of retributive justice, famously summarized by the principle "an eye for an eye, a tooth for a tooth," which aimed to maintain social stability by equating the severity of punishment to the nature of the crime.
The Fall of Hammurabi's Empire and the Fragmentation of Mesopotamia
Despite Hammurabi's remarkable achievements and the prosperity that marked his reign, the Babylonian Empire quickly unraveled after his death. His successor struggled to maintain the vast territories that Hammurabi had conquered, and the empire soon fragmented into smaller, rival kingdoms and independent city-states. Political instability and infighting characterized this period, as no single ruler could unify the region as effectively as Hammurabi had.
Nevertheless, the legacy of Hammurabi's code endured. Even as political unity dissolved, the legal principles he established continued to influence Mesopotamian society for over a thousand years. These laws were adopted and adapted by successive rulers, becoming a cornerstone of legal systems throughout the region. The written language, Akkadian, and the cuneiform script of Sumerian origin also remained widespread, providing a cultural and linguistic link between the fragmented states.
Environmental Challenges and the Decline of Southern Mesopotamia
While political fragmentation was one challenge facing the region, environmental changes also played a crucial role in shaping Mesopotamia's fate. The southern part of Mesopotamia, where once-thriving cities like Ur and Uruk had stood, faced severe droughts that significantly altered the landscape. Over time, this once-fertile region became arid and desolate, unable to support the agricultural productivity that had sustained its early civilizations.
The decline in agricultural output led to economic difficulties and the gradual depopulation of these southern cities. Communities migrated northward or to other regions where conditions were more favorable for farming and trade. This environmental shift not only weakened the local economies but also diminished the influence of southern Mesopotamian culture, even as its religious beliefs and legal traditions, such as those codified by Hammurabi, continued to resonate throughout the wider region.
Hammurabi's Lasting Influence on Civilization
Hammurabi's impact on the ancient world extended far beyond his military conquests and the brief supremacy of Babylon. His codification of laws influenced not only subsequent Mesopotamian societies but also legal traditions in cultures across the ancient Near East. The principles outlined in his code are considered a precursor to modern legal systems, emphasizing the importance of justice, accountability, and the rule of law.
Through his legislative achievements, Hammurabi demonstrated a visionary approach to governance, one that sought to bring cohesion to a diverse and often fractious population. His legacy is a testament to the idea that civilization thrives not just on conquest and power but also on the establishment of fair and equitable systems that govern everyday life. Despite the eventual fall of his empire, Hammurabi's contributions to law and governance left an indelible mark on human history, shaping the development of legal and social norms for centuries to come.
Last update: October 11, 2024
Go to definitions: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z
 DONATE
DONATE 
See also: